
How does your company treat workplace safety?
Who ensures that work is completed safely?
How do you think your organization can improve workplace safety and reduce hazards?
These are some of the questions that employees are asked in a workplace safety survey.
Industries like manufacturing, construction, health-care and few others, need to have strict safety norms.
This is because the nature of these jobs involves the use of heavy machinery, hazardous chemicals and dangerous processes.
Even a “regular” office requires certain basic safety measures to be put in place.
Ergonomic furniture, fire safety, basic first aid kits and so on are some basic safety measures.
Now, in a pandemic stricken world, more measures like sanitization, temperature checks, masks and social distancing are being put in place.
Safety Checklists are paper based or digital documents used during a safety inspection of a workplace or site.
The inspection is carried out primarily to identify potential hazards at the location.
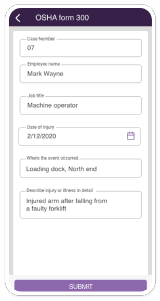
OSHA or Occupational Safety and Health Administration is a regulatory and compliance body of health and safety in America.
OSHA came into being in 1970 mainly to monitor and regulate the health and safety of workers.
They do this by imposing workplace standards, training and additional guidance.
OSHA standards are guidelines that define means that establishments need to use to guard their personnel from hazards.
As per OSHA rulebooks, businesses must keep their workplaces free of severe documented hazards.
OSHA has listed out a varied array of checklists for the identification of possible dangers in different industries.
There are OSHA criteria for construction work, maritime operations and general industry (applies to most sites).
These guidelines limit the quantity of harmful chemicals that workers can be exposed to.
They also require establishments to deploy precautionary measures, equipment and constant supervision of activities.
Examples of some safety standards are: warranting safety within restricted spaces, fall protection, prevention and control of contagious diseases, check exposure to harmful chemicals, machine guards, and so on.
Mandatory safety training for risky jobs is another stringent guideline.
Frontline workers in the manufacturing industry are often exposed to dangerous environments and situations.
Safety precautions are a crucial aspect of manufacturing establishments.
The safer a manufacturing facility is the more productive it will be.
Dangerous practices left unchecked at a facility lead to losses in both reputation and bottomline.
It’s important to understand manufacturing safety from the point of view of how it impacts your workers as well as your turnover.
That brings us to our focal point – what does manufacturing safety mean?
It means that all workers are able to go about their day to day work without worrying about the risk of falling ill, becoming hurt or seriously injured.
Does this mean they can just rest easy and do their jobs with a sense of abandon?
No. It means that every worker is well trained and made aware of all the precautions, technology and steps needed to ensure that they remain safe during the course of their workday.
This requires constant caution and training on the part of the company.
Research has shown that businesses that prioritize Environmental Health and Safety (EHS) display higher efficiency and productivity than the industry average.
On the contrary, those that have a weak safety program experience more incidents and fall slightly lower on the performance index.
Manufacturers that care about the safety and wellbeing of their workers often turn out to be high performing units.
These manufacturers have rigorous safety programs.
The programs entail a combination of training, surveying, communication, regular reports, inspections, auditing and preventive measures.
Data collection and analysis is another crucial aspect of implementing safety protocol.
Manufacturing units usually employ a large number of deskless workers.
These workers are exposed to hazards like machines, dangerous chemicals and materials.
Manufacturing safety needs to address aspects like functional measures for lathes, drills, presses, and other machines.
Protective gear like PPE (personal protective equipment), gloves, goggles, boots, should be abundantly accessible to workers.
Safe storage of materials, correct way of using tools and materials and frequent cleaning should be taught in a manufacturing safety training program.
Since safety is a core part of manufacturing, adopting a tool that unifies all angles of a safety program will come in handy.
It helps if businesses digitize the process through a mobile-first tool that assists with training, documentation, tracking, alerting, managing and analysing data.
The tool should be secure and mobile-first since most people in manufacturing are deskless workers and frontline staff.
These workers don’t operate from behind a desk, meaning they usually don’t have workstations, laptops or personal computers to work out of.
Therefore, their only point of access to digital tools is their mobile phone.
Hence, a robust, smooth, mobile friendly safety checklist and safety management technology goes a long way in plugging this gap.
Self-inspection checklists are periodically updated by OSHA.
Some checklists that OSHA provides to industries are: occupational injury and illness reports, radiation safety, explosion, fall protection, electrical related, fire emergency related safety, tools and machinery and so on.
Supervisors have to check all the boxes during an audit. This is to ensure every protocol in the OSHA handbook is adequately addressed.
1. Personal Protective Equipment
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) are not just an outcome of COVID-19.
PPE is used in shop floors where protection is needed from identifiable hazards.
Employers need to make an assessment to determine the kind of PPE and the personnel that need to don this equipment.
Regular checks also need to be performed.
Other PPE related OSHA guidelines state that workers need to be trained on PPE procedures.
Some other PPE related aspects to be addressed in this safety checklist include:
This is the sample of the PPE related OSHA checklist. However, now even COVID related precautionary measures are factored into this safety checklist.
2. Health, Safety and First Aid
A health and safety program is a popular OSHA checklist that needs to be adopted on a manufacturing shop floor.
A manufacturing safety and health program needs to factor in hazard management within a generic health and safety check.
Businesses usually chart out detailed plans in this regard.
These plans should entail training, specifications, and other requirements that are mandatory in a workplace of this nature.
Some general questions in an OSHA first aid checklist could be:
Is there a trained member of the personnel in charge of implementing the safety and first aid program?
Is a database of hospitals in the vicinity available, and do staff have access to numbers and details of nearby hospitals in the event of an emergency?
Are first-aid kits available at specific stations and are they checked and renewed on a frequent basis?
Do workers get training in basic first aid before being inducted?
Are workers aware of the availability of first aid and do they know how to access it when required?
Is there a process in place to address employee grievances with respect to first aid, health and safety concerns?
3. Facilities Management
The shop floor and overall facility is an essential element in manufacturing industries.
For one, these jobs require workers to be on site.
Remote working is out of the question in a production or assembly unit.
Most workers here are deskless workers or frontline staff.
To manage a manufacturing unit, businesses should ensure the facility is clean and sanitary.
All hazardous materials, chemicals and debris need to be cleaned up periodically and properly.
The waste materials need to be disposed of in a proper and safe manner, according to regulations.
As applicable to all workplaces, a well-organized housekeeping system should be kept in place.
Groupe.io has successfully deployed automated checklists for housekeeping staff at various facilities.
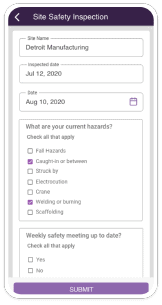
Passages and aisles need to be kept clean and marked appropriately.
The passageways should be designed appropriately and periodic boards and signs should be placed to signal any dangers in terms of proximity to equipment, materials or other hazards.
Other generic questions in OSHA checklist of facilities management of a manufacturing facility are:
Is dust routinely removed from surfaces?
Are stairs and stairways of the right dimensions and height?
Is there an employee training program for fire safety and handling harmful substances?
4. Flammable Materials and Fire Safety
Managing flammable materials is a major part of the safety program in a manufacturing unit.
Combustible and flammable materials and waste products need to be properly stored and this OSHA safety checklist needs to factor in these details.
Correctly storing and stocking flammable substances is the key to reducing the risk of a fire erupting on the premises.
Flammable liquids and solvents need to be stored in fireproof containers at all times.
Most importantly, employees need to be trained in fire safety.
5. Material Storage Mechanism and Facilities
Material storage might be common to many industries, but has to be carefully dealt with in a manufacturing shop floor.
Some concerns during storing materials in manufacturing include – safety clearance, security of storage space and removal of hazards in storage areas.
Personnal should also ensure that hazardous chemicals are not stored close to heat sources.
6. Electrical
Electrical wiring needs to follow the local and national code for building, owning, operating and maintenance.
Grounding is of utmost importance and machines need to be well grounded as per OSHA safety standards.
Double insulation is preferable.
Junction boxes need to be protected well and extension chords have to be kept in safe proximity to heavy machinery.
So Groupe.io is definitely an all round productivity and communications tool for frontline manufacturing workers.
Digital Checklists are a core aspect of Groupe’s productivity features.
Groupe’s digital checklists let you convert paper based to paperless checklists in no time.
They also help supervisors track work progress, identify bottlenecks and ensure compliance all from a mobile device.
Safety checklists can easily be accessed, processed and reviewed through Groupe.io’s slick user interface.
More importantly, the platform onboards deskless and frontline staff without a corporate email address.
It is secure and GDPR and HIPAA compliant, and rolls out in 24 hours!
Want to know more about how Groupe.io’s safety checklists can enhance your company’s safety culture? Login for a quick and free demo here! Or also, just write to us with your queries at [email protected]!